Lua 类型
虽然本篇主要讲 table,不过在那之前,最好先来认识一下 Lua 其他类型在 Lua解释器中的实现。
UserData 暂且不谈,NUMBER细分为浮点数和整数,字符串则分长短字符串,函数又分Lua函数和C函数还有轻量的C函数,这一部分会分别留到字符串和闭包的时候再谈论。
#define LUA_TNIL 0
#define LUA_TBOOLEAN 1
#define LUA_TLIGHTUSERDATA 2
#define LUA_TNUMBER 3
#define LUA_TSTRING 4
#define LUA_TTABLE 5
#define LUA_TFUNCTION 6
#define LUA_TUSERDATA 7
#define LUA_TTHREAD 8
#define LUA_TNUMFLT (LUA_TNUMBER | (0 << 4)) /* float numbers */
#define LUA_TNUMINT (LUA_TNUMBER | (1 << 4)) /* integer numbers */
#define LUA_TSHRSTR (LUA_TSTRING | (0 << 4)) /* short strings */
#define LUA_TLNGSTR (LUA_TSTRING | (1 << 4)) /* long strings */
#define LUA_TLCL (LUA_TFUNCTION | (0 << 4)) /* Lua closure */
#define LUA_TLCF (LUA_TFUNCTION | (1 << 4)) /* light C function */
#define LUA_TCCL (LUA_TFUNCTION | (2 << 4)) /* C closure */Table
先来想想,我们一般是怎么使用 table 的,是不是大部分时候都是既用来当数组又用来当哈希表。
因此,可以很简单的想到,table 很有可能底层是使用哈希表来实现的。事实上Lua早期版本也确实是这么做的,只不过后来优化了 table 被当做数组用的性能(就是加了个数组)。
可以看到 Table 的结构中,有表示 metatable,也有数组,还有哈希表,跟我们猜想的几乎一致。而且这还更激进一点,两者都启用!
注意到 lsizenode 是以2位低的整数次幂,非实际大小。
typedef struct Table {
....
lu_byte flags; /* 1<<p means tagmethod(p) is not present */
lu_byte lsizenode; /* log2 of size of 'node' array */ // 以2为底表示哈希表大小
unsigned int sizearray; /* size of 'array' array */
TValue *array; /* array part */
Node *node;
Node *lastfree; /* any free position is before this position */
struct Table *metatable;
....
} Table;数组部分没什么好看的,我们主要看其哈希表的实现。 TKey 中的 nk 主要是用来当Key的哈希值相同时,开链用。
typedef union TKey {
struct {
TValuefields;
int next; /* for chaining (offset for next node) */
} nk;
TValue tvk;
} TKey;
typedef struct Node {
TValue i_val;
TKey i_key;
} Node;创建 table
创建 table 主要是对结构进行初始化,同时注意到一点,table 的 node 默认是 dummynode,在lua设计中,当一个table的哈希表部分为空时,则默认使用一个 dummynode 的全局对象,因为是只读访问,没有线程安全问题,其实设置成 NULL 我想也是可以的,不过还记得上面的 lsizenode 是以2为底的幂次吗?2^0 == 1,因此设置一个 dummynode,逻辑看起来更自然。不过如果你不小心链接了两次 Lua 库,内存上就有两份 dummynode,根据 dummynode 运算的逻辑都将是 未定义行为。
#define dummynode (&dummynode_)
static const Node dummynode_ = {
{NILCONSTANT}, /* value */
{{NILCONSTANT, 0}} /* key */
};
static void setnodevector (lua_State *L, Table *t, unsigned int size) {
if (size == 0) { /* no elements to hash part? */
t->node = cast(Node *, dummynode); /* use common 'dummynode' */
t->lsizenode = 0;
t->lastfree = NULL; /* signal that it is using dummy node */
}
....
}
Table *luaH_new (lua_State *L) {
GCObject *o = luaC_newobj(L, LUA_TTABLE, sizeof(Table));
Table *t = gco2t(o);
t->metatable = NULL;
t->flags = cast_byte(~0);
t->array = NULL;
t->sizearray = 0;
setnodevector(L, t, 0);
return t;
}数组还是哈希表?
经过以上,我们可能会思考,我对这个table的操作,到底是操作了数组还是哈希表?在这里我们来看看以下几个操作。
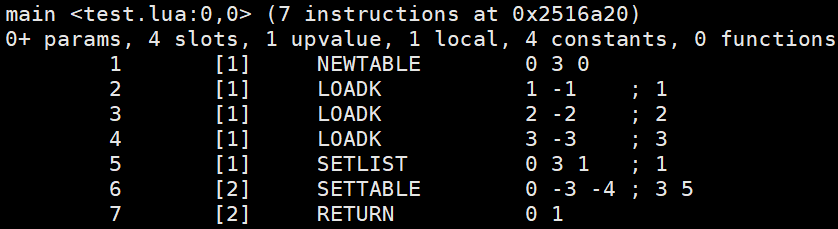
local a = {1, 2, 3}
a[3] = 5可以看出,第一行的操作指令是 SETLIST,而第二行则是 SETTABLE 。
SETLIST
SETLIST 这种操作默认是在 数组中的,因此会先检查 table 中数组的大小,然后进行赋值。 luaH_setint 会调用 luaH_newkey 通过哈希获取 Key 应当存在的位置,然后将其放入。
vmcase(OP_SETLIST) {
int n = GETARG_B(i);
int c = GETARG_C(i);
unsigned int last;
Table *h;
if (n == 0) n = cast_int(L->top - ra) - 1;
if (c == 0) {
lua_assert(GET_OPCODE(*ci->u.l.savedpc) == OP_EXTRAARG);
c = GETARG_Ax(*ci->u.l.savedpc++);
}
h = hvalue(ra);
last = ((c-1)*LFIELDS_PER_FLUSH) + n;
if (last > h->sizearray) /* needs more space? */
luaH_resizearray(L, h, last); /* preallocate it at once */
for (; n > 0; n--) {
TValue *val = ra+n;
luaH_setint(L, h, last--, val);
luaC_barrierback(L, h, val);
}
L->top = ci->top; /* correct top (in case of previous open call) */
vmbreak;
}luaH_resize 会对数组和哈希表进行扩容or缩容,数组中 nil的值 将会被省略。
SETTABLE
这个操作就得根据情况来判断了,但最终都是调用到了 luaH_newkey 这个函数。如果不是个 table,则检查其元方法是否存在,检查方法就是根据 table 结构中的 flags 字段按位来找是否有元方法。查找元方法的路径不能过长,默认是 MAXTAGLOOP 2000。
#define MAXTAGLOOP 2000
void luaV_finishset (lua_State *L, const TValue *t, TValue *key,
StkId val, const TValue *slot) {
int loop; /* counter to avoid infinite loops */
for (loop = 0; loop < MAXTAGLOOP; loop++) {
const TValue *tm; /* '__newindex' metamethod */
if (slot != NULL) { /* is 't' a table? */
Table *h = hvalue(t); /* save 't' table */
lua_assert(ttisnil(slot)); /* old value must be nil */
tm = fasttm(L, h->metatable, TM_NEWINDEX); /* get metamethod */
if (tm == NULL) { /* no metamethod? */
if (slot == luaO_nilobject) /* no previous entry? */
slot = luaH_newkey(L, h, key); /* create one */
/* no metamethod and (now) there is an entry with given key */
setobj2t(L, cast(TValue *, slot), val); /* set its new value */
invalidateTMcache(h);
luaC_barrierback(L, h, val);
return;
}
/* else will try the metamethod */
}
else { /* not a table; check metamethod */
if (ttisnil(tm = luaT_gettmbyobj(L, t, TM_NEWINDEX)))
luaG_typeerror(L, t, "index");
}
/* try the metamethod */
if (ttisfunction(tm)) {
luaT_callTM(L, tm, t, key, val, 0);
return;
}
t = tm; /* else repeat assignment over 'tm' */
if (luaV_fastset(L, t, key, slot, luaH_get, val))
return; /* done */
/* else loop */
}
luaG_runerror(L, "'__newindex' chain too long; possible loop");
}luaH_newkey
根据 哈希规则,找到 mp即在哈希表中应该存放key的位置,如果被用掉了,就检查占据这个位置的键的位置是不是真的就在这(通过哈希,你可以理解为线性探查法),若真在这,就通过左移 lastfree 指针,找一个新位置,然后将其链起来。否则的话,老让给新的,老重新哈希找到合适的位置,如果还冲突继续往左走。(我个人觉得像是 线性探查+开链法的结合体)
TValue *luaH_newkey (lua_State *L, Table *t, const TValue *key) {
Node *mp;
TValue aux;
if (ttisnil(key)) luaG_runerror(L, "table index is nil");
else if (ttisfloat(key)) {
lua_Integer k;
if (luaV_tointeger(key, &k, 0)) { /* does index fit in an integer? */
setivalue(&aux, k);
key = &aux; /* insert it as an integer */
}
else if (luai_numisnan(fltvalue(key)))
luaG_runerror(L, "table index is NaN");
}
mp = mainposition(t, key);
if (!ttisnil(gval(mp)) || isdummy(t)) { /* main position is taken? */
Node *othern;
Node *f = getfreepos(t); /* get a free place */
if (f == NULL) { /* cannot find a free place? */
rehash(L, t, key); /* grow table */
/* whatever called 'newkey' takes care of TM cache */
return luaH_set(L, t, key); /* insert key into grown table */
}
lua_assert(!isdummy(t));
othern = mainposition(t, gkey(mp));
if (othern != mp) { /* is colliding node out of its main position? */
/* yes; move colliding node into free position */
while (othern + gnext(othern) != mp) /* find previous */
othern += gnext(othern);
gnext(othern) = cast_int(f - othern); /* rechain to point to 'f' */
*f = *mp; /* copy colliding node into free pos. (mp->next also goes) */
if (gnext(mp) != 0) {
gnext(f) += cast_int(mp - f); /* correct 'next' */
gnext(mp) = 0; /* now 'mp' is free */
}
setnilvalue(gval(mp));
}
else { /* colliding node is in its own main position */
/* new node will go into free position */
if (gnext(mp) != 0)
gnext(f) = cast_int((mp + gnext(mp)) - f); /* chain new position */
else lua_assert(gnext(f) == 0);
gnext(mp) = cast_int(f - mp);
mp = f;
}
}
setnodekey(L, &mp->i_key, key);
luaC_barrierback(L, t, key);
lua_assert(ttisnil(gval(mp)));
return gval(mp);
}如果 getfreepos 找不到合适的位置(lastfree 走到最左边),则 调用 rehash。
里面会统计数组大小,哈希表中可以合入数组的大小(就是看一下key是不是能转换成整数)。
static void rehash (lua_State *L, Table *t, const TValue *ek) {
unsigned int asize; /* optimal size for array part */
unsigned int na; /* number of keys in the array part */
unsigned int nums[MAXABITS + 1];
int i;
int totaluse;
for (i = 0; i <= MAXABITS; i++) nums[i] = 0; /* reset counts */
na = numusearray(t, nums); /* count keys in array part */
totaluse = na; /* all those keys are integer keys */
totaluse += numusehash(t, nums, &na); /* count keys in hash part */
/* count extra key */
na += countint(ek, nums);
totaluse++;
/* compute new size for array part */
asize = computesizes(nums, &na);
/* resize the table to new computed sizes */
luaH_resize(L, t, asize, totaluse - na);
}Table 长度怎么算?
Lua 中取长度采用 # 号获取,它会调用以下函数。
如果存在数组部分,则采用二分查找找到第一个 t[i] ≠nil && t[i + 1] = nil,如果数组真的全在里面,才会走到哈希表的计算。isdummy 为 ((t)->lastfree == NULL) ,如果哈希表部分为空,就不算哈希部分呗,如果有,就在哈希表里面二分查找,将整数下标中的个数给加入进来。因此永远不要对非序列进行取长度操作。
static lua_Unsigned unbound_search (Table *t, lua_Unsigned j) {
lua_Unsigned i = j; /* i is zero or a present index */
j++;
/* find 'i' and 'j' such that i is present and j is not */
while (!ttisnil(luaH_getint(t, j))) {
i = j;
if (j > l_castS2U(LUA_MAXINTEGER) / 2) { /* overflow? */
/* table was built with bad purposes: resort to linear search */
i = 1;
while (!ttisnil(luaH_getint(t, i))) i++;
return i - 1;
}
j *= 2;
}
/* now do a binary search between them */
while (j - i > 1) {
lua_Unsigned m = (i+j)/2;
if (ttisnil(luaH_getint(t, m))) j = m;
else i = m;
}
return i;
}
lua_Unsigned luaH_getn (Table *t) {
unsigned int j = t->sizearray;
if (j > 0 && ttisnil(&t->array[j - 1])) {
/* there is a boundary in the array part: (binary) search for it */
unsigned int i = 0;
while (j - i > 1) {
unsigned int m = (i+j)/2;
if (ttisnil(&t->array[m - 1])) j = m;
else i = m;
}
return i;
}
/* else must find a boundary in hash part */
else if (isdummy(t)) /* hash part is empty? */
return j; /* that is easy... */
else return unbound_search(t, j);
}MetaMethod
前面提到过,table 的结构有个 flags 字段,表示哪些元方法不存在!然后对 一个类型操作时,会去检查其元方法,如果有元方法,则尝试调用,最多调用2000次,超过则抛出错误。同时会对 元方法的名字,进行优化,提前创建好这些字符串对象,并将其缓存起来。
void luaT_init (lua_State *L) {
static const char *const luaT_eventname[] = { /* ORDER TM */
"__index", "__newindex",
"__gc", "__mode", "__len", "__eq",
"__add", "__sub", "__mul", "__mod", "__pow",
"__div", "__idiv",
"__band", "__bor", "__bxor", "__shl", "__shr",
"__unm", "__bnot", "__lt", "__le",
"__concat", "__call"
};
int i;
for (i=0; i<TM_N; i++) {
G(L)->tmname[i] = luaS_new(L, luaT_eventname[i]);
luaC_fix(L, obj2gco(G(L)->tmname[i])); /* never collect these names */
}
}pairs与ipairs
table 最常用的两种遍历操作,pairs 是通过 luaH_next 函数实现的。当key 为nil时,则从头开始遍历。
int luaH_next (lua_State *L, Table *t, StkId key) {
unsigned int i = findindex(L, t, key); /* find original element */
for (; i < t->sizearray; i++) { /* try first array part */
if (!ttisnil(&t->array[i])) { /* a non-nil value? */
setivalue(key, i + 1);
setobj2s(L, key+1, &t->array[i]);
return 1;
}
}
for (i -= t->sizearray; cast_int(i) < sizenode(t); i++) { /* hash part */
if (!ttisnil(gval(gnode(t, i)))) { /* a non-nil value? */
setobj2s(L, key, gkey(gnode(t, i)));
setobj2s(L, key+1, gval(gnode(t, i)));
return 1;
}
}
return 0; /* no more elements */
}需要注意的是,如果 table 中某个键的值被设置为nil,有可能会被GC回收,但是此时还在遍历,Lua官方称其为死键。
其实也没做什么特殊的,标志为死键又不是被删除了,不过如果被 rehash 则会被从哈希表清除,触发 rehash 的条件是添加新键且空间不够了,因此如果你不添加新键,遍历就挺安全的。
static unsigned int findindex (lua_State *L, Table *t, StkId key) {
unsigned int i;
if (ttisnil(key)) return 0; /* first iteration */
i = arrayindex(key);
if (i != 0 && i <= t->sizearray) /* is 'key' inside array part? */
return i; /* yes; that's the index */
else {
int nx;
Node *n = mainposition(t, key);
for (;;) { /* check whether 'key' is somewhere in the chain */
/* key may be dead already, but it is ok to use it in 'next' */
if (luaV_rawequalobj(gkey(n), key) ||
(ttisdeadkey(gkey(n)) && iscollectable(key) &&
deadvalue(gkey(n)) == gcvalue(key))) {
i = cast_int(n - gnode(t, 0)); /* key index in hash table */
/* hash elements are numbered after array ones */
return (i + 1) + t->sizearray;
}
nx = gnext(n);
if (nx == 0)
luaG_runerror(L, "invalid key to 'next'"); /* key not found */
else n += nx;
}
}
}至于 ipairs 则是通过 lua_geti 实现,其真正的操作是在 luaH_getint 中,如果还是找不到,则会通过 luaV_finishget 去找其元方法。ipairs 当遍历到 nil 时则会停止,要特别注意不能有黑洞。
LUA_API int lua_geti (lua_State *L, int idx, lua_Integer n) {
StkId t;
const TValue *slot;
lua_lock(L);
t = index2addr(L, idx);
if (luaV_fastget(L, t, n, slot, luaH_getint)) {
setobj2s(L, L->top, slot);
api_incr_top(L);
}
else {
setivalue(L->top, n);
api_incr_top(L);
luaV_finishget(L, t, L->top - 1, L->top - 1, slot);
}
lua_unlock(L);
return ttnov(L->top - 1);
}

Comments | NOTHING
该文章已经关闭评论